Discover cloud seeding: a weather modification novel innovative technology that safely and sustainably changes rain patterns all over the world.
"By using seeding, you start rain formation process when particles are introduced into clouds and consequent bursting of droplet aggregation leading to precipitation."
Cloud seeding, a kind of "weather engineering", as well as a technology that promises to enable mankind to enhance or mitigate atmospheric phenomena has been on many agendas of scientists, policymakers, and the general audience for a long time. It is a pioneering method that embraces the use of substances meant for modifying the components of clouds by affecting the natural activities of clouds, with the only goal being to spark precipitation or other activities of meteorology. Despite the circumambient interest and skepticism, the principles, practices, and applications of cloud seeding must be well-elucidated as such information is mandatory in maneuvering the role of cloud seeding in tackling water shortages, regulating weather patterns, and minimizing the impacts of droughts and other associated weather problems.
What is Cloud Seeding?
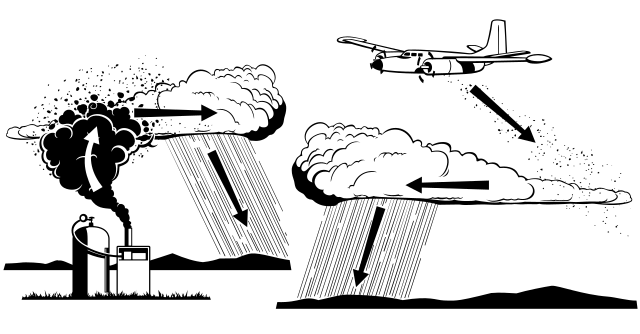
Cloud seeder is a conscious attempt to modify a natural phenomenon of water vapor condensation and precipitation. It generally refers to the spraying of agents, which are commonly known as cloud seeding materials, into clouds where it helps in the development and enlargement of ice particles of water droplets. The most common cloud-seeding particles are silver iodide, potassium iodide, and liquid propane. These stuff behave like around which can ice crystals, or water droplets that form, increase the production of precipitation, and are a source of it.
How Does Seeding by Clouds Happen?
It works on the principle that when hygroscopic material is brought into the atmosphere, water molecules in the air get attracted to the surface and condense or even freeze leading to precipitation. Silver iodide, in this case, has a structural buildup that resembles the ice, which results in it becoming an effective nucleus for ice crystal formation in supercooled clouds. After they have been consumed by the formed clouds, the seeding agents contribute to the creation of ice crystals and water particles, which in turn facilitate the formation of precipitation.
When and Where is Cloud Seeding Conducted?
Cloud seeding is often carried out in areas, or countries experiencing scarcity of water resources such as in agriculture, hydroelectricity plants, or the city water supply. It is usually used in semi-arid or arid regions where the natural rainfall is not that much, such as the southwest of the United States, Australia, the Middle East, and Central Asia. The climatic condition suitable for cloud formation and precipitation is often the specific condition under which the cloud seeding operations are commonly carried out such as in convective clouds or orographic clouds.
Applications and Challenges
Through its broad specter of possible implementations, cloud seeding can provide solutions to multiple problems encountered when supplying water, for the lowlands, the mountainous regions, and when the drought and wildfires occur. On the one hand, while its therapeutic potential is evident, the way it raises different questions concerning its efficacy and effects on the environment have been discussed and researched so along. The Fundamental issue of uncertainty is about long-term consequences on weather patterns, ecosystems, and human health. Supporters emphasize that further studies should be conducted to know the consequences, but criticism persists on the possible unintended outcomes. This could include localized flooding, changes in rainfall patterns, and ecological rather than economic disruptions.
Cloud seeding by its nature provides scientists, engineers, and resource managers with an exciting opportunity to deal with the problems associated with water shortages and extreme weather worlds over. Although cloud seeding as a topic of inquiry and debate is still being subjected to research and advances catalyzed by technological developments, it is the one that may prove to be useful in curbing the adverse effects on the environment and rest the rain or snow in case of deficiency. With our growing expertise on cloud dynamics plus atmospheric processes, soon enough we will be able to make safe and environmentally sustainable use of cloud seeding technology.
More On Cloud Seeding